

In general, HDDs are capable of storing larger amounts of data at a lower cost per gigabyte.įor example, an Acer Aspire laptop with a 1-terabyte HDD costs around the same as the similar Acer Aspire with a 128-gigabyte SSD. Given their superior speed and processing ability, SSDs may be preferable for NACE member institutions, as well as those that may be considering taking the leap into esports. Since its founding in 2016, the National Association of College Esports has grown to more than 130 member institutions and more than 3,000 student-athletes. What may have initially been viewed as a fad has blossomed into a real force on college campuses. On the gaming frontier, speed is essential. Another consideration when determining hard drive needs is t he emergence of college esports. The retrieval process for SSDs, on the other hand, is electronic, allowing them to quickly access data.Īn HDD will still get you to the same information you need, but it can take more physical movement - not to mention more time and greater latency - to do so. In order to access data, an HDD’s mechanical arm has to move to the right location on the storage platter to locate specific data. The main advantage of SSDs lies in their ability to access data electronically rather than electromechanically, which results in fast booting and transfer speeds. Ultimately, speed is one of the main factors in evaluating drive types. This component plays a significant role in the drive’s read/write speed, which is a key factor in separating a drive with a decent read/write speed from one with an excellent one. Reading and writing is performed by an embedded processor called a controller. Rather, they are similar to USB sticks in that they store data on microchips. With SSDs, on the other hand, there are no moving parts. For example, a typical laptop drive spins at 5,400 rpm or 7,200 rpm, while some server-based drives can go as high as 15,000 rpm.

The faster the spin, the faster the HDD’s performance. The primary difference between HDD and SSD is physical, specifically in the way that they physically read and write data onto the disk.įirst introduced in 1956, HDDs use magnetism to store data on a rotating platter with a read/write head floating above that spinning platter. MORE FROM EDTECH: Check out three ways universities can find the perfect solid state drive solution. The question of whether to select solid-state drives (SSD) or hard disk drives (HDD) has become more pressing of late, as higher education institutions look for ways to improve the speed and reliability of their computing systems while keeping costs in check.īelow are some things to consider when weighing the pros and cons of each drive type.
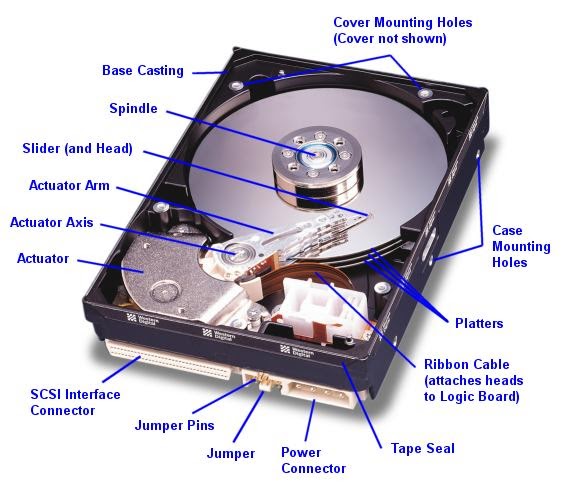
When it comes to selecting the PCs, laptops and servers that will power higher education institutions, administrators face a number of choices, including the type of drive that powers these technologies.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
